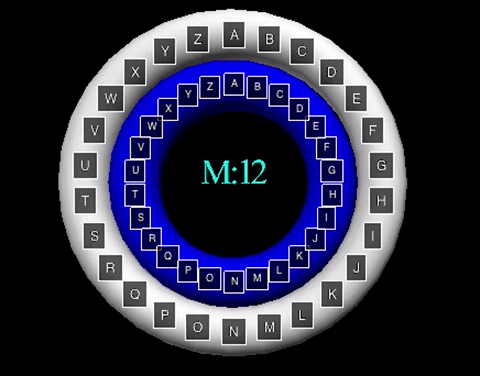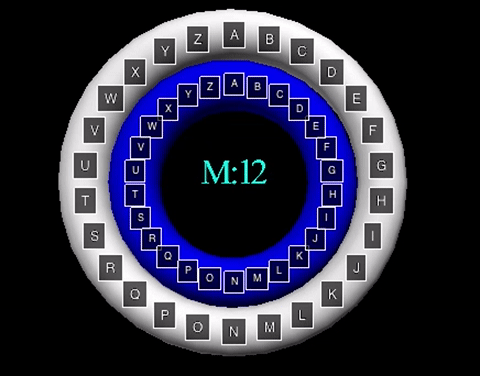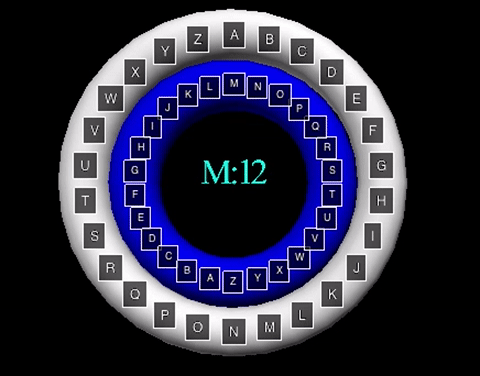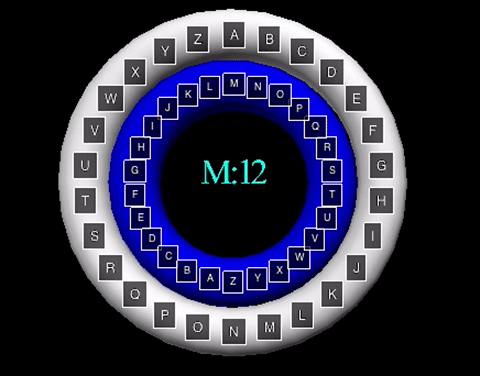
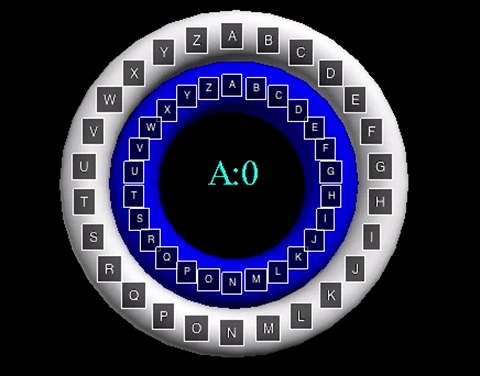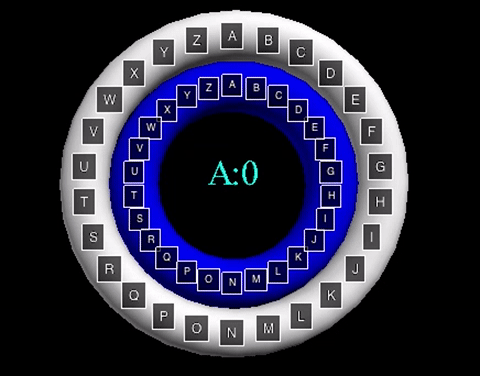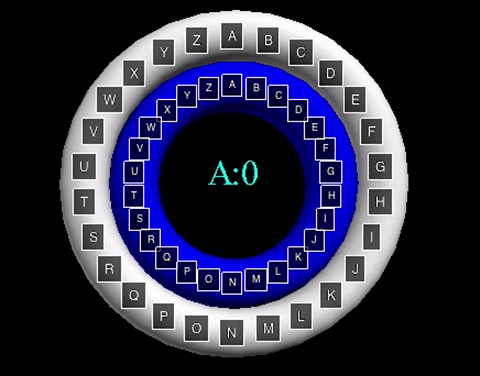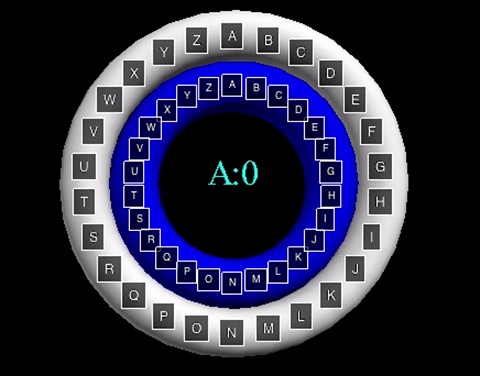
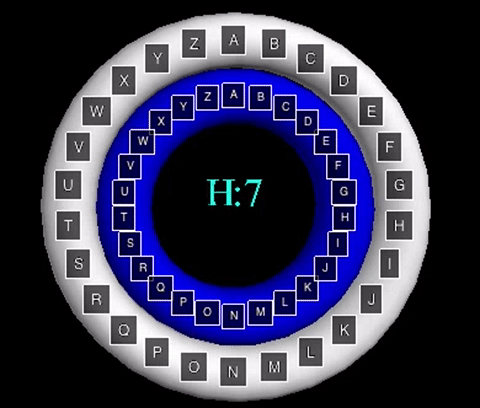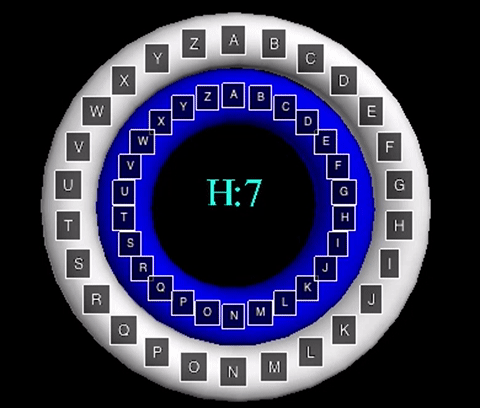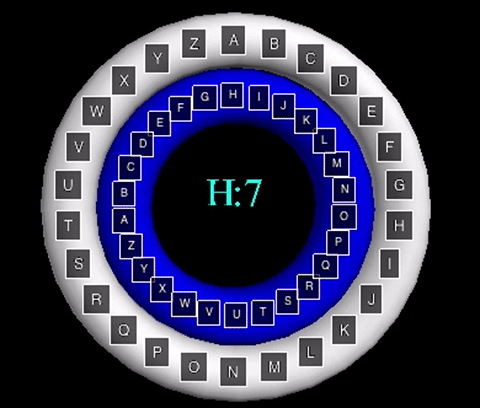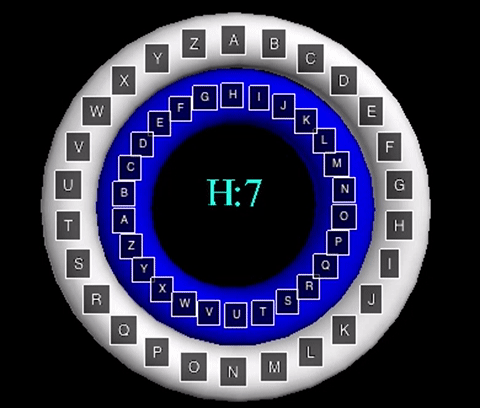
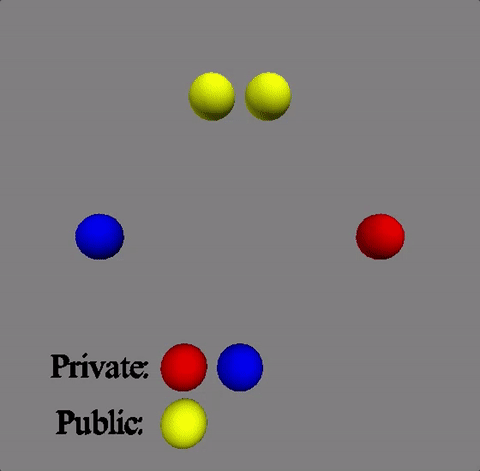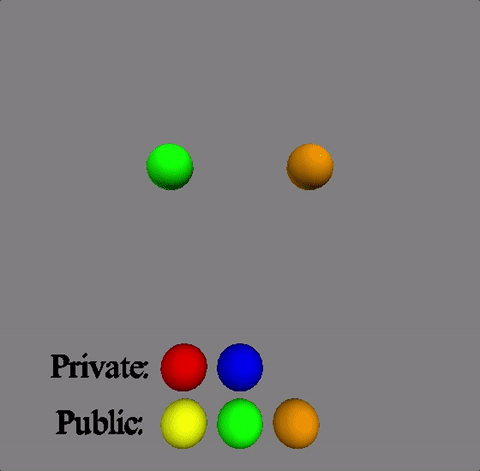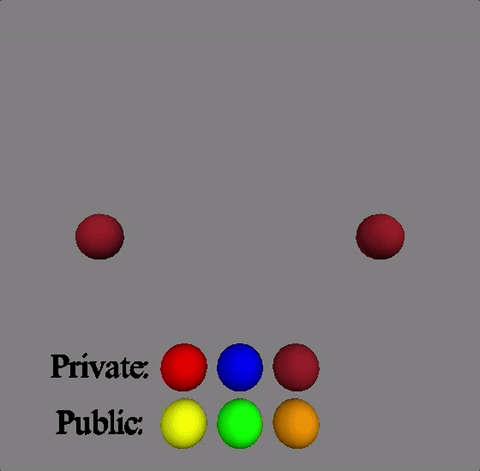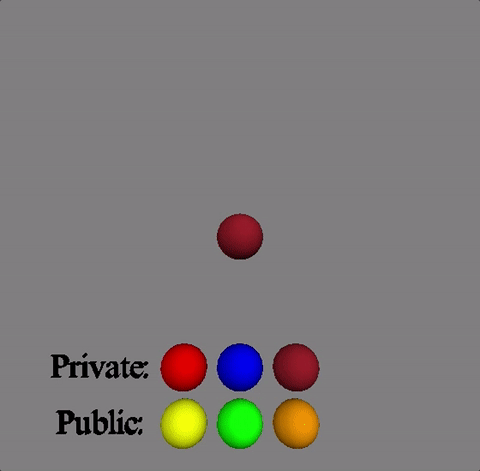
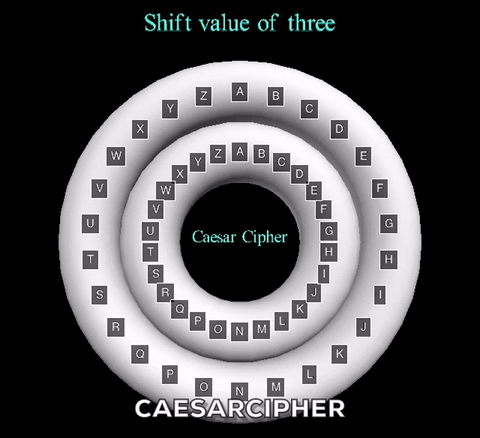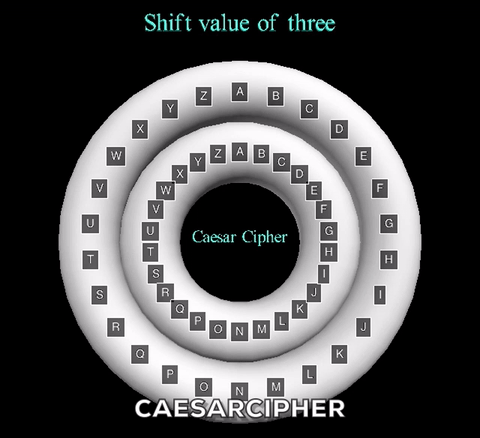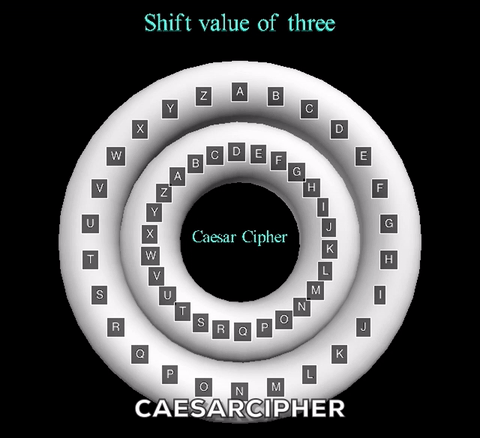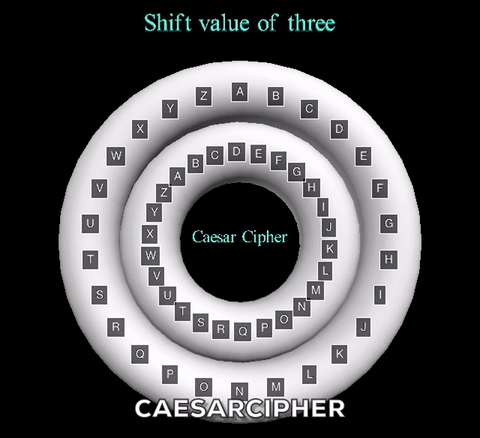
The animation displayed displays a shift value of three. The inner wheel spins, allowing the letters on the outside wheel to align with their respective shift letters.
Cryptography is the study of processing, storing, and transmitting data into a particular encrypted form that only those for whom the message is intended will be able to decode and process the message. This is usually done through the use of ciphers. While the first recorded use of encryption dates back to Ancient Rome with the Caesar Cipher, encryption has developed far beyond simple alphabetic substitutions.
For my project, I want to explore cryptography and the visualization of different encryption methods through graphics using VPython. First, I will explore ancient cryptography, including the Caesar Cipher method and the Vigenére cipher. At this point, I look to creating a visualization of these by creating spinning wheels to display the encryption shifts. Then, I would like to delve further into more modern encryption methods, like public-key encryption. The creation process of my graphics to present the visualizations may evolve and thus, this part of my project is currently flexible to best fit the encryption methods I study since this project has not been attempted previously.
Through visualizing encryption, I hope to make learning and understanding the concepts behind various encryption methods easier and less abstract.
The Caesar Cipher is a simple shift cipher used by Julius Caesar in 58 B.C.
to protect sensitive military information from interception by enemy forces.
This ancient method of encryption is a mono-alphabetic substitution, meaning
the shift replacement is constant throughout the encryption process. Messages
are encrypted through sliding the letters in a given message a set shift value
down the alphabet. For example, with a shift value of 3, the string "ABCDEF"
would become "DEFGHI" with 'A' shifting down three letters to be substituted
with 'D', 'B' with 'E', and so on.

The animation displayed displays a shift value of three. The inner wheel spins, allowing
the letters on the outside wheel to align with their respective shift letters.

The poly-alphabetic cipher, also known as the Vigenère cipher, uses multiple letter shifts,
rather than only one like the Caesar Cipher. Instead of choosing a shift value, a shift word
is chosen. Each letter of the word corresponds to a number in the alphabet with 'A' starting
at 0 to 'Z' at 25. For example, if the shift word is "CAT", this would correspond to 2, 0,
19 in the alphabet. These numbers become the shift values for the message so if the message
"HELLO" was to be sent, 'H' would be shifted 2, 'E' shifted 0, 'L' shifted 19, 'L' shifted 2,
and so on. The end result of using the poly-alphabetic cipher on the word "HELLO" with a
shift word of "CAT" is "JEENO". Essentially, the poly-alphabetic cipher is multiple
Caesar Ciphers, whose shift value is determined by the corresponding letter in the key
shift word.
The animation displayed displays the cipher using the key word "MATH". The inner wheels spin
to align the outer letters with their respective shifts, like that of the Caesar Cipher animation.
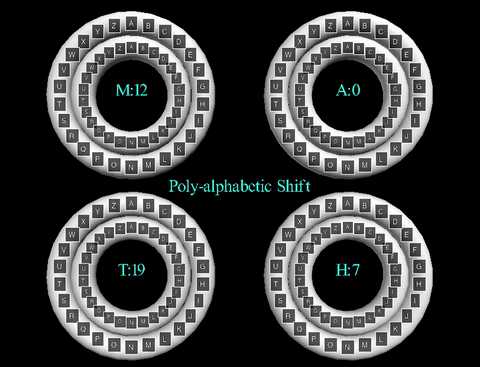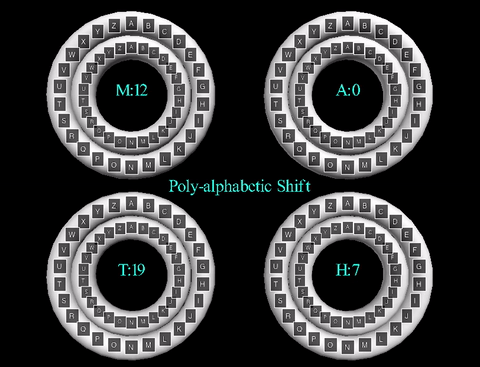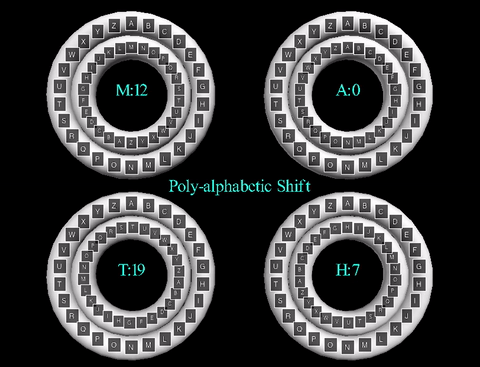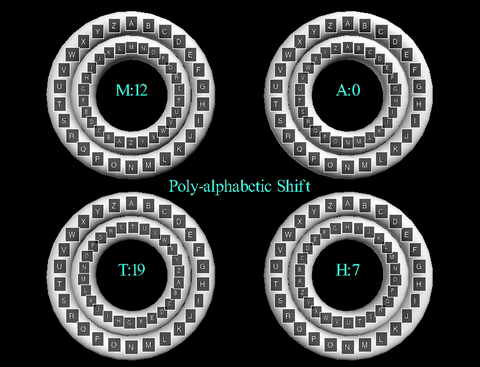
Here are each of the wheels displayed individually: